Interstellar Objects Like ‘Oumuamua:
In October 2017, a strange visitor from beyond our solar system captivated astronomers and sparked global intrigue: ‘Oumuamua, the first confirmed interstellar object to pass through our cosmic neighbourhood. Unlike anything seen before, this cigar-shaped wanderer defied typical comet or asteroid behaviour, fuelling debates about its origins—could it be an alien spacecraft or a natural relic from another star? Since then, Interstellar Objects Like ‘Oumuamua: History, Discoveries, and Cosmic Mysteries , discoveries like 2I/Borisov and the recent 3I/ATLAS in 2025 have deepened our fascination with interstellar objects.
This blog post explores the history and discoveries of interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua, answering key questions such as “What are interstellar objects?” and “Why do they matter?” We’ll dive into their detection, characteristics, scientific significance, and even the tantalizing theories about extra-terrestrial technology. Optimized for SEO, AEO, and AI searchability, this guide offers clear, concise facts and insights for curious minds in 2025.
What Are Interstellar Objects?
Interstellar objects are celestial bodies that originate outside our solar system and travel through it, unbound by the Sun’s gravitational pull. Unlike comets or asteroids born in our cosmic backyard, these objects follow hyperbolic orbits, meaning they zip in, pass by, and exit without orbiting the Sun. Their high speeds and unique trajectories betray their alien origins, often ejected from distant star systems millions of years ago.
Key Characteristics of Interstellar Objects
- Origin: Formed around other stars, possibly in planetary systems or debris disks.
- Orbit: Hyperbolic, not elliptical, indicating they’re just visiting.
- Composition: Varies—some are icy like comets, others rocky or metallic.
- Speed: Often exceed 30 miles per second (108,000 mph), far faster than solar system objects.
- Size: Range from hundreds of feet to tens of miles wide.
This answers the query: “What are interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua?” They’re rare cosmic travellers offering clues about the universe beyond our solar system.
The Discovery of ‘Oumuamua: A Historic Milestone
How Was ‘Oumuamua Found?
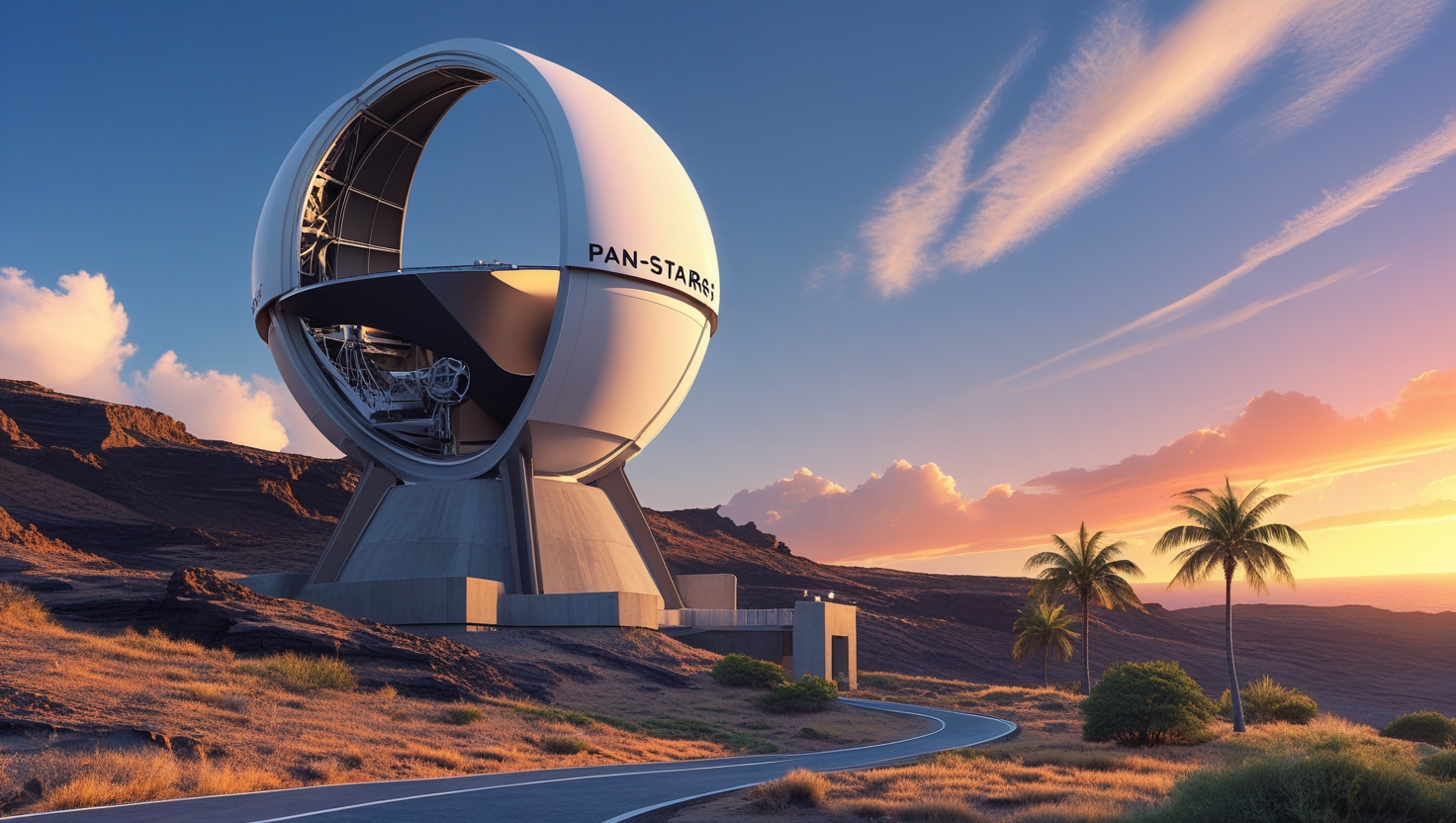

On October 19, 2017, the Pan-STARRS1 telescope in Hawaii spotted an unusual object moving at 54 miles per second (196,000 mph). Named ‘Oumuamua (Hawaiian for “scout” or “messenger”), it was initially mistaken for a comet but lacked a visible coma or tail, puzzling astronomers. Its trajectory confirmed it as the first interstellar object ever detected.
- Discovery Date: October 19, 2017.
- Location: Detected by Pan-STARRS1, Maui, Hawaii.
- Speed: ~196,000 mph at discovery.
- Size: Estimated 1,300–2,600 feet long, elongated like a cigar.
- Path: Passed within 0.25 AU (23 million miles) of Earth in November 2017.
Why Was ‘Oumuamua Significant?
‘Oumuamua’s discovery was a game-changer. It proved interstellar objects could reach our solar system, opening a new field of study. Its odd shape and unexpected acceleration (without visible outgassing) led to speculation about artificial origins, notably from Harvard’s Avi Loeb, who suggested it might be an alien probe.
This section addresses: “What was the first interstellar object discovered?”
Other Interstellar Objects: 2I/Borisov and 3I/ATLAS
2I/Borisov: The Second Visitor
In August 2019, amateur astronomer Gennadiy Borisov discovered the second interstellar object, named 2I/Borisov. Unlike ‘Oumuamua, this object behaved like a typical comet, with a visible coma and tail, confirming its icy composition.
- Discovery Date: August 30, 2019.
- Size: About 0.6–1.2 miles wide.
- Speed: ~110,000 mph at closest approach.
- Closest Approach: 1.9 AU (177 million miles) from Earth in December 2019.
- Significance: Showed interstellar comets can resemble solar system ones, unlike ‘Oumuamua’s anomalies.
3I/ATLAS: The 2025 Sensation
Discovered on July 1, 2025, by the ATLAS telescope in Chile, 3I/ATLAS is the third confirmed interstellar object. Its massive size (12–19 miles wide) and high speed (133,200 mph) have reignited debates about interstellar visitors, with Avi Loeb again proposing it could be alien technology.
- Discovery Date: July 1, 2025.
- Size: 12–19 miles in diameter.
- Speed: 37 miles/second (133,200 mph).
- Closest Approach: ~17 million miles from Earth in late 2025.
- Significance: Its size and minimal outgassing fuel both scientific and speculative interest.
This answers: “What are the known interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua?”
Why Do Interstellar Objects Matter?
Interstellar objects are cosmic time capsules, carrying clues about distant star systems. Studying them helps us understand:
- Stellar System Formation: Their composition reveals how planets and debris form elsewhere.
- Galactic Dynamics: Their paths trace interactions between stars and ejected material.
- Planetary Defense: Detection systems for interstellar objects improve our ability to spot near-Earth threats.
- Extraterrestrial Life: Anomalies like ‘Oumuamua’s acceleration spark searches for artificial signals.
For those asking, “Why are interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua important?” they bridge our solar system to the wider galaxy, advancing science and exploration.
The Alien Hypothesis: Are Interstellar Objects Artificial?
Avi Loeb’s theories about ‘Oumuamua and 3I/ATLAS as potential alien probes have captured public imagination. He cites ‘Oumuamua’s unusual shape, lack of comet-like outgassing, and non-gravitational acceleration as evidence of possible artificial design. For 3I/ATLAS, its size and minimal tail add to the speculation.
Pros of the Alien Hypothesis
- Explains anomalies not fully accounted for by natural models.
- Aligns with SETI’s mission to find extraterrestrial technology.
- Encourages innovative thinking about cosmic visitors.
Cons of the Alien Hypothesis
- Most scientists attribute anomalies to natural processes (e.g., hydrogen outgassing).
- No radio signals or artificial structures detected.
- Occam’s razor favors simpler, natural explanations.
This addresses: “Could interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua be alien spacecraft?”
How Are Interstellar Objects Detected?
Detecting interstellar objects requires advanced telescopes and rapid response systems. Here’s how it works:
- Telescope Surveys: Systems like Pan-STARRS, ATLAS, and LSST scan the sky for moving objects.
- Trajectory Analysis: Hyperbolic orbits signal interstellar origins.
- Follow-Up Observations: Radar, spectroscopy, and space telescopes (e.g., Hubble) analyze composition and speed.
- Data Sharing: Global networks like NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office coordinate findings.
For voice queries like “How do scientists find interstellar objects?” this process ensures early detection and tracking.
Challenges in Studying Interstellar Objects
- Speed: Their high velocities give astronomers little time to observe.
- Distance: They often pass far from Earth, limiting detailed study.
- Rarity: Only three confirmed objects in eight years make data scarce.
- Technology Limits: Current telescopes struggle to capture fine details of fast-moving, distant objects.
This answers: “What are the challenges in studying interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua?”
Future of Interstellar Object Research
The discovery of ‘Oumuamua, 2I/Borisov, and 3I/ATLAS has spurred investment in detection technology. Upcoming projects include:
- Vera C. Rubin Observatory: Its Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) could find dozens of interstellar objects by 2030.
- Interception Missions: Concepts like ESA’s Comet Interceptor aim to study future visitors up close.
- SETI Integration: Enhanced radio surveys to check for artificial signals.
For those asking, “What’s next for interstellar object research?” these advancements promise more discoveries.
FAQ: Common Questions About Interstellar Objects Like ‘Oumuamua
What is an interstellar object?
An interstellar object is a celestial body from outside our solar system, traveling through on a hyperbolic orbit.
What was the first interstellar object discovered?
‘Oumuamua, detected on October 19, 2017, by the Pan-STARRS1 telescope in Hawaii.
How many interstellar objects have been discovered?
Three: ‘Oumuamua (2017), 2I/Borisov (2019), and 3I/ATLAS (2025).
Could ‘Oumuamua be an alien spacecraft?
While Harvard’s Avi Loeb suggests it’s possible due to its anomalies, most scientists believe it’s a natural object.
How are interstellar objects detected?
Using telescopes like Pan-STARRS and ATLAS, which identify hyperbolic orbits and confirm with follow-up observations.
Why are interstellar objects important?
They reveal details about other star systems, improve planetary defense, and spark questions about extraterrestrial life.
Will we see more interstellar objects soon?
Yes, observatories like the Vera C. Rubin LSST may detect dozens in the coming decade.
Conclusion
Interstellar objects like ‘Oumuamua, 2I/Borisov, and 3I/ATLAS are rare glimpses into the galaxy’s vastness. From their historic discoveries to their scientific and speculative significance, they challenge our understanding of the cosmos. As detection technology advances, we’re poised to uncover more of these wanderers, each carrying stories from distant stars. Stay curious—follow updates on space exploration and share your thoughts on these cosmic mysteries!
For more on interstellar visitors, check our posts on planetary defense or SETI’s search for alien life. What do you think these objects are? Comment below!
